Ear infections (otitis)
Here is a brief informative overview of the different types of otitis.
Otitis externa
o Otitis externa is an infection of the external part of the ear, mainly at the level of the ear canal. It is characterized by pain and sometimes purulent drainage. It rarely causes fever. Swimming and use of ear swabs are risk factors. The treatment is cleaning of the ear under the microscope, the placement of a « wick » dressing, and antibiotic drops. Antibiotics by mouth are generally not necessary. In diabetics, otitis exerne can become complicated as malignant otitis externa which is an infection of the bone, and requires treatment with intravenous antibiotics.
Otitis media
o Otitis media is an infection of the part of the ear behind the eardrum. It is often preceded by a cold and can be accompanied with sinusitis. It produces intense pain, hearing loss, and sometimes purulent discharge due to a perforation in the eardrum. It is much more common in children, but is possible in adults. Examination of the back of the nose using a camera by an Otolaryngologist is necessary to eliminate a mass that blocks the drainage of the middle ear through the Eustachian tube (tube that links the nose to the ear). The treatment is generally antibiotics by mouth if otitis persists more than 48 hours. When otitis media produces complications (such as facial paralysis or meningitis), or when children have repeatd bouts of otitis medial, the treatment can include the surgical placement of myringotomy tubes.
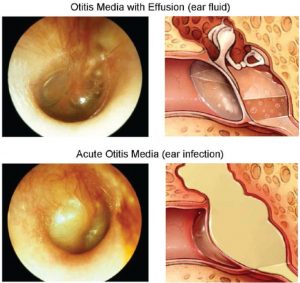
Serous otitis media
Serous otitis media is the presence of non-infected fluid behind the eardrum that causes hearing loss. This fluid most often resorbs spontaneously within three months. However, in young children, persistent fluid can cause speech delay. In these cases, we sometimes recommend placement of ear tubes.
Our doctors at the Clinique ORL are available to evaluate and treat you for all these conditions

