What to do when your nose is bleeding?
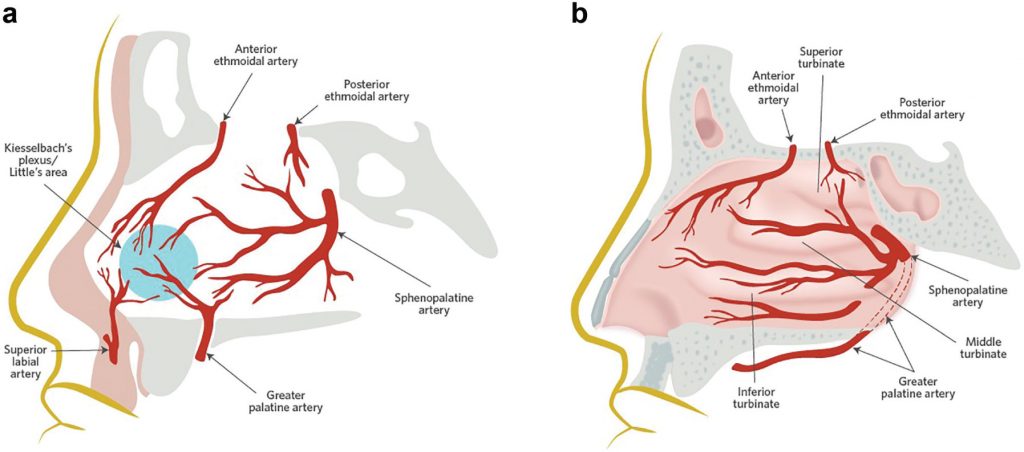
The medical term for nosebleed is "epistaxis". Most often, bleeding comes from the front of the nose, where many small blood vessels near the surface of the nasal septum warm the air you inhale. In most cases, nosebleeds affect only one nostril, but if the problem is severe, blood can sometimes come from both nostrils (and even an eye).
Most nosebleeds can be easily controlled at home. You have to sit upright and lean your head forward to prevent the blood from sinking to the back of your throat. Swallowing blood may cause vomiting. With your thumb and your forefinger on the soft part of the nose, just below the bone bridge, pinch the nostrils for 10 minutes without interruption. Do not put anything in the nostril, but the use of a decongestant nasal spray (oxymetazoline or xylometazoline type) in the short term may help to cause a constriction of the blood vessel involved. To prevent the bleeding from happening again, do not hit your nose soon after. Do not bend down and avoid forcing during a few hours.
La plupart des saignements de nez mineurs peuvent être facilement contrôlés à la maison. Ne vous étendez pas. Asseyez-vous droit et penchez légèrement vos hanches en avant pour empêcher le sang de couler à l’arrière de la gorge. Avaler du sang peut provoquer des vomissements. En mettant votre pouce et votre index sur la partie molle du nez, juste sous le pont osseux, pincez les narines pendant 10 minutes sans interruption. Ne mettez rien dans la narine, mais l’utilisation d’un spray nasal décongestionnant à court terme peut aider à contracter le vaisseau coupable. Pour empêcher que le saignement recommence, ne vous mouchez pas rapidement après. Ne vous penchez pas et évitez les activités pénibles, ainsi que les travaux lourds pendant quelques heures.
If self-treatment is not effective and if the bleeding persists for more than 20 minutes, or if a nose bleed is a result of a facial injury, you should see a doctor. Medical treatment of difficult nosebleeds may require cauterizing the bleeding vessel with a chemical such as silver nitrate or with electrocautery. Nasal packing is also an option.
Moistening the air you breathe or moistening the inside of the nose with a gel or with petroleum jelly can help prevent bleeding. Avoid intense bloating, sneeze with your mouth open and do not try to clear the nose with an object like a Q-tip.
